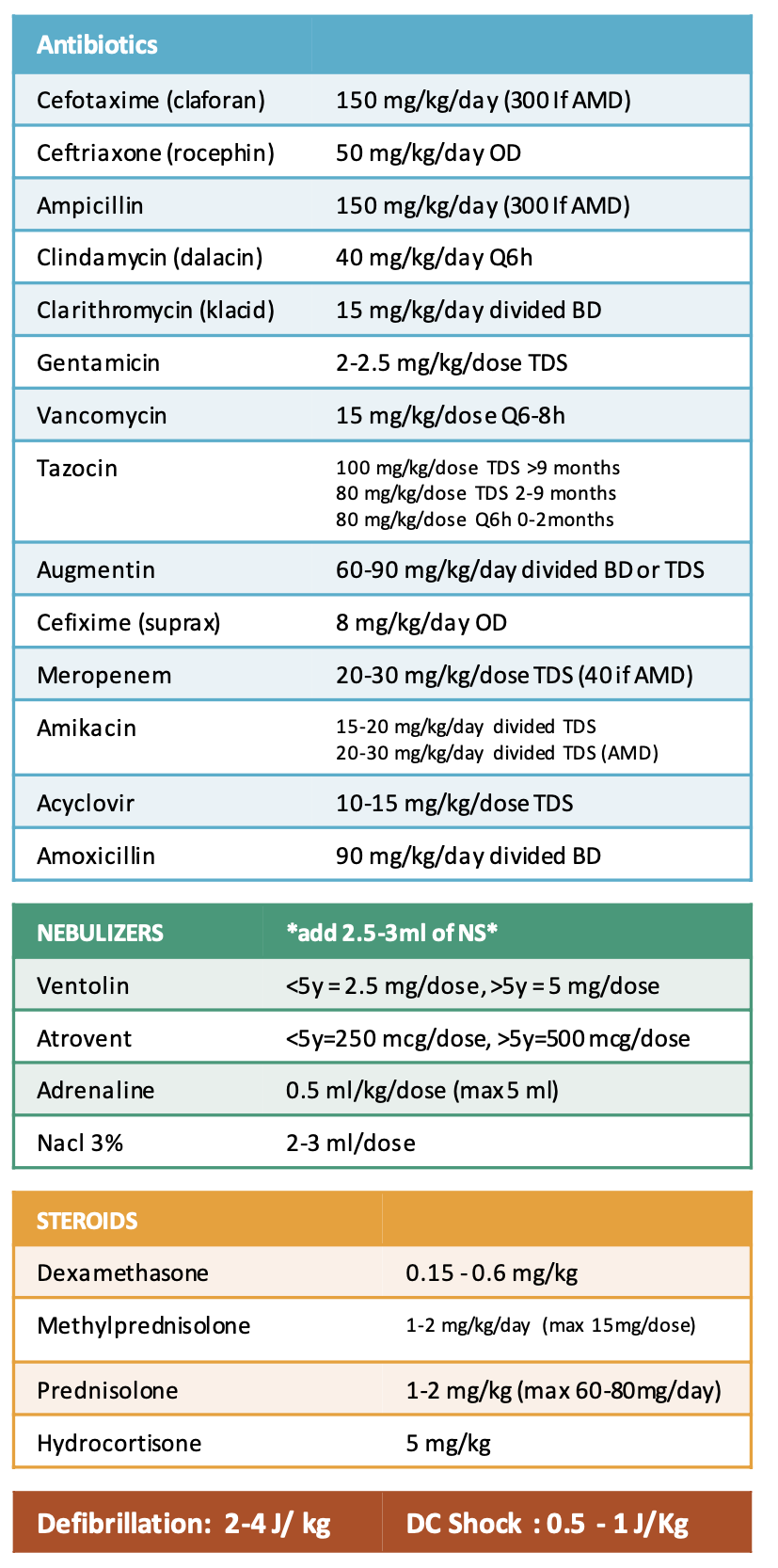
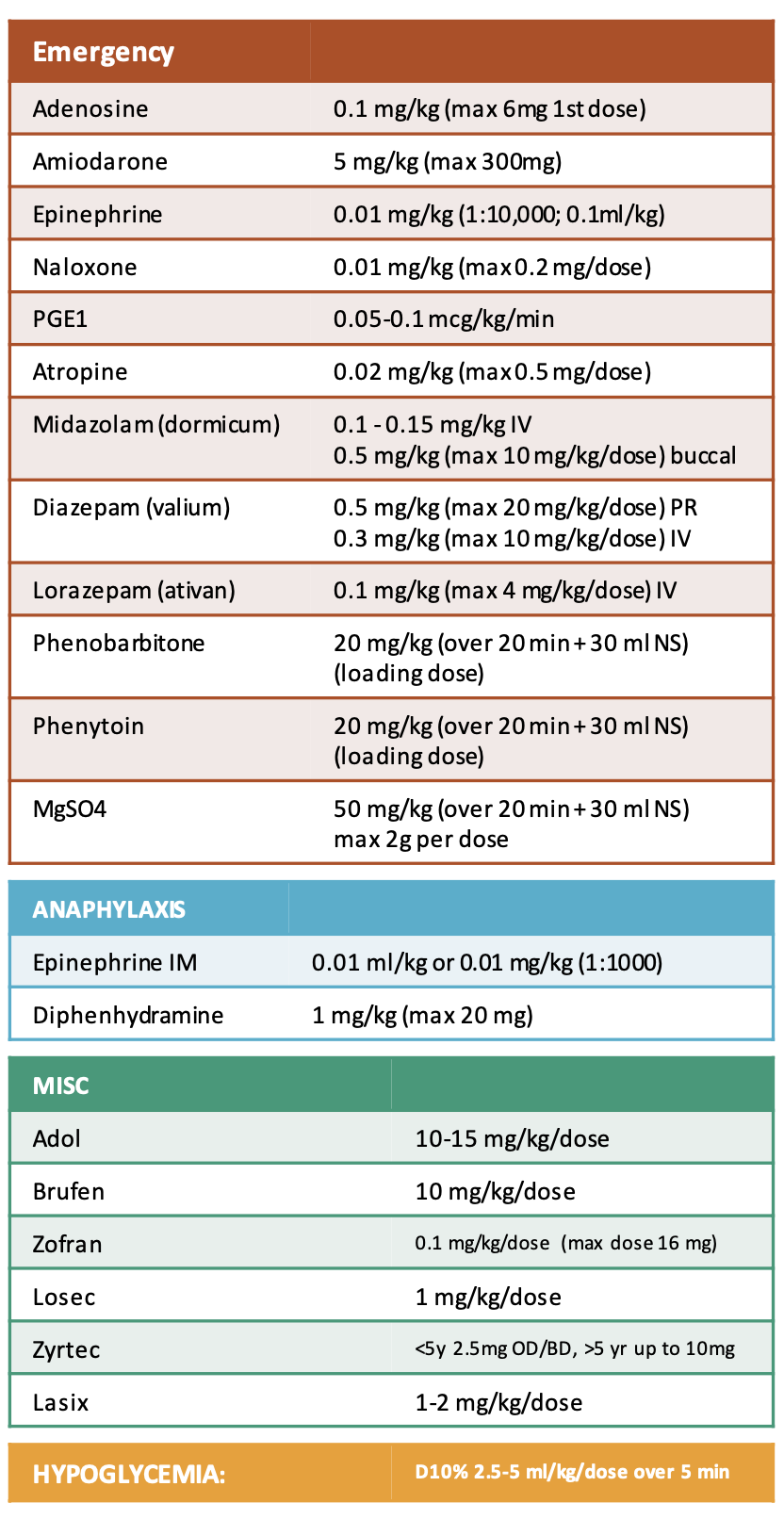
Dosages of the common medications:
Tamiflu (oseltamivir) dosing for children is based on age and weight. Here are the general dosing recommendations for both treatment and prophylaxis:
Tamiflu Treatment Dosage (for influenza)
Infants < 1 year:
3 mg/kg/dose twice daily.
Children ≥ 1 year:
≤ 15 kg: 30 mg twice a day.
> 15 to 23 kg: 45 mg twice a day.
> 23 to 40 kg: 60 mg twice a day.
> 40 kg: 75 mg twice a day.
Duration: 5 days.
Tamiflu Prophylaxis Dosage
Children < 3 months: Not recommended unless in critical situations.
Children 3 months to < 1 year:
3 mg/kg/dose once daily.
Children ≥ 1 year:
≤ 15 kg: 30 mg once daily.
15 to 23 kg: 45 mg once daily.
23 to 40 kg: 60 mg once daily.
> 40 kg: 75 mg once daily.
Duration: 7 days after last known exposure.
Calculating IV fluids for pediatric patients involves determining maintenance requirements, deficit replacement, and accounting for ongoing losses. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Maintenance Fluids
Use the Holliday-Segar Formula to calculate daily maintenance fluid requirements based on the child’s weight:
Body WeightFluid RequirementFirst 10 kg100 mL/kg/dayNext 10 kg50 mL/kg/day>20 kg20 mL/kg/day
For hourly rate: Divide the total by 24.
Example:
A 15 kg child:
First 10 kg: 10×100=1000 mL/day10×100=1000mL/day
Next 5 kg: 5×50=250 mL/day5×50=250mL/day
Total: 1000+250=1250 mL/day1000+250=1250mL/day or 125024=52 mL/hr241250=52mL/hr.
2. Deficit Replacement
To replace dehydration, estimate the fluid deficit based on the degree of dehydration:
Mild (3–5%): 30–50 mL/kg
Moderate (6–9%): 60–90 mL/kg
Severe (≥10%): 100+ mL/kg
Deficit Calculation:
Deficit Volume=Weight (kg)×%dehydration×10Deficit Volume=Weight (kg)×%dehydration×10.
Replace the deficit over 24–48 hours (e.g., 50% in the first 8 hours, then the rest in 16–24 hours).
Example:
A 15 kg child with 6% dehydration:
15×0.06×10=900 mL15×0.06×10=900mL.
3. Ongoing Losses
Account for ongoing losses (e.g., diarrhea, vomiting):
Replace estimated losses mL for mL using ORS or IV fluids.
4. Total Fluid Requirement
The total fluid rate combines:
Maintenance fluids.
Deficit replacement.
Ongoing losses.
5. Type of Fluid
Maintenance: Use isotonic fluids (e.g., 0.9% saline + 5% dextrose or Ringer's lactate with dextrose).
Deficit/Ongoing losses: Use isotonic fluids (e.g., 0.9% saline or Ringer's lactate).
Example Calculation
A 12 kg child with 5% dehydration, mild ongoing diarrhea (~200 mL/day):
Maintenance:
10×100+2×50=1100 mL/day10×100+2×50=1100mL/day.Deficit:
12×0.05×10=600 mL12×0.05×10=600mL.Ongoing losses: ~200 mL.
Total in 24 hours:
1100+600+200=1900 mL/day1100+600+200=1900mL/day or 190024≈79 mL/hr241900≈79mL/hr.
6. Monitoring
Reassess hydration status frequently.
Monitor urine output (1–2 mL/kg/hour is normal).
Check electrolytes to avoid complications like hypernatremia or hyponatremia.