CARDIOLOGY
CARDIOLOGY
Here are the most common cardiac emergencies in paediatrics and how to manage them:
Reminder: If you feel overwhelmed or in doubt please contact your senior for help.
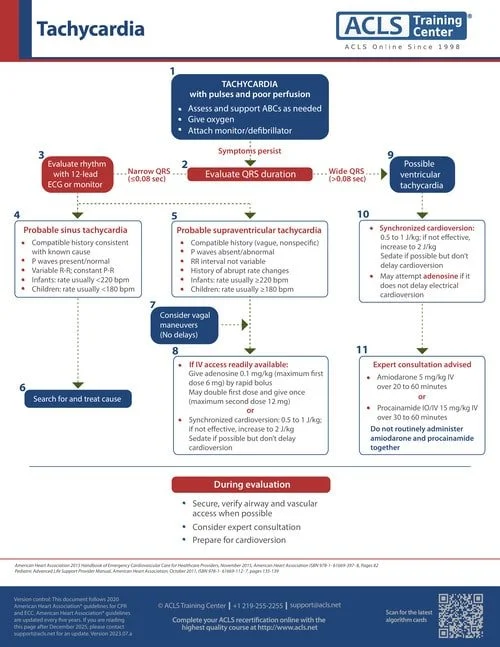
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in children is the most common arrhythmia encountered in pediatrics.
ECG Features of SVT in a Child
Heart Rate:
Rapid, typically >220 bpm in infants and >180 bpm in older children.
Regular rhythm in most cases.
P Waves:
Often absent or not clearly visible because they are buried in the preceding T wave.
If visible, they may appear inverted in leads II, III, and aVF (retrograde conduction).
QRS Complex:
Narrow QRS complexes (<120 ms) in most cases (orthodromic SVT).
Wide QRS complexes can occur with aberrant conduction or pre-existing bundle branch block.
RR Interval:
Regular intervals; the rhythm is typically regular (unlike irregular rhythms seen in atrial fibrillation).
Abrupt Onset and Termination:
SVT starts and ends suddenly (paroxysmal).
ST-T Changes:
May show ST depression or subtle repolarization abnormalities due to the rapid heart rate.
Differential Diagnosis
Sinus Tachycardia:
Gradual onset/offset, identifiable P waves, rate <220 bpm in infants or <180 bpm in children.
Atrial Flutter:
Sawtooth pattern of flutter waves.
Ventricular Tachycardia:
Wide QRS complexes and AV dissociation.
Management During ECG Recognition
Assess hemodynamic stability:
If unstable (hypotension, poor perfusion, altered mental state), proceed with synchronized cardioversion.
If stable, attempt vagal maneuvers (ice to face, blowing into a syringe).
Adenosine:
If vagal maneuvers fail, administer adenosine IV (0.1 mg/kg, max 6 mg; can increase to 0.2 mg/kg, max 12 mg).
Continuous Monitoring:
Record ECG during rhythm changes for further evaluation.
Prompt recognition and management of SVT on ECG are crucial to avoid complications and restore normal rhythm.